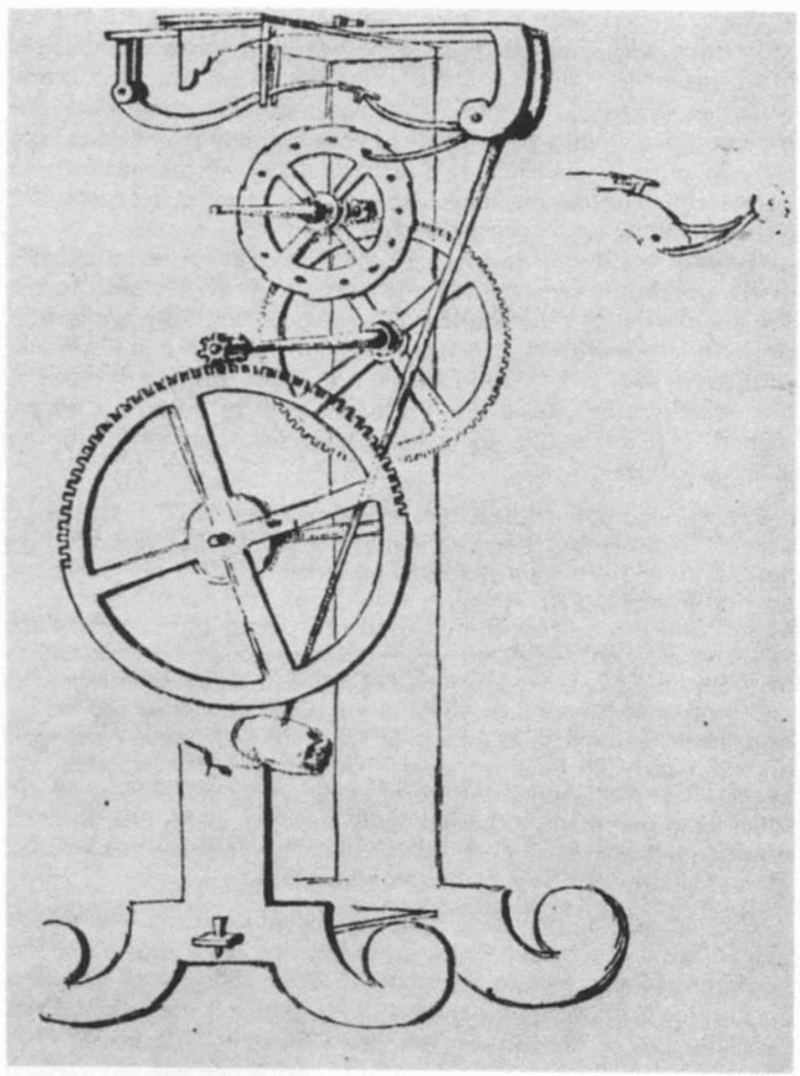Galileo (full name, Galileo Galilei) was born in Pisa in 1564. Widely considered to be one of the founders of astronomical observation and modern physics, he was a strong supporter of Copernicus’s heliocentric model. Having enrolled to study medicine at the University of Pisa, he went against the wishes of his father, a music theorist, and instead studied mathematics, a discipline which included physics and astronomy. He would later obtain the chair of mathematics at the University of Padua in 1592. Several years prior to this, Galileo had observed the isochronism of the pendulum, i.e. its period is independent of amplitude. Late in life, he would use these observations to devise a pendulum clock with a specific “duplex” escapement, which his son built for him. Throughout his years lecturing students in Padua, Galileo continued to busy himself with experiments. He also made a number of navigational instruments and, having studied falling bodies, described the corresponding mathematical formula.
In 1609 Galileo heard that a spectacle-maker in the Netherlands had invented an instrument that made distant objects appear closer. This prompted him to make his own telescope, an instrument he refined and would use to study the stars, the Moon, sunspots and Jupiter’s satellites. These observations confirmed his belief that the Copernican model was correct, but his defence of these ideas angered the Church to the point that he was ordered not to hold, teach or defend the heliocentric model. The election in 1623 of Pope Urban VIII, a friend and patron of Galileo, allowed him greater freedom to develop his theories, until the publication in 1632 of Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems sparked further trouble. For having sought to prove Earth’s motion, Galileo was summoned to appear before the Inquisition. Old and abandoned by all, he recanted. Galileo was assigned to residence in Arcetri where he wrote his Dialogues Concerning Two New Sciences. He died in 1642.
1583
Aged 19, Galileo observed the isochronism of the pendulum, i.e. period is independent of amplitude.
1609
Built a telescope with a convergent objective lens and a divergent eyepiece lens which magnified objects up to 30 times and is known today as a Galilean telescope.
1641
Gave the design for his pendulum clock to his son, Vincenzio, who began its construction in 1649 but died before it was completed.
1992
Before the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, the Vatican formally rehabilitated Galileo, stating that the trial had been marked by “tragic incomprehension”.